If you’ve ever been at sea or to a seaside, you’ve undoubtedly wondered, “How did all this water get here?” as you gazed out at the vast ocean. The solution dates back to the formation of Earth about 4.5 billion years ago. Water-rich planetesimals and other bodies brought water to our still-developing planet in those early days. That argument appears to be supported by the recent discovery of a previously unrecognized population of such asteroids between Mars and Jupiter.
An international group of geoscientists used the N.A.S.A Infrared Telescope in Hawaii to measure the spectra of these so-called “low-albedo” (or “dark”) worldlets. The characteristics of the light reflected off their surfaces show what chemical elements and minerals exist there. From those measurements, the research team created a model of the newly found asteroids.

Measuring Dark Asteroids
According to Dr. Driss Takir, an astrophysicist at the N.A.S.A Johnson Space Center and the study’s lead author, “The astronomical measurements allow the identification of Ceres-like asteroids with a diameter as small as 100 kilometers, currently located in a confined region between Mars and Jupiter near Ceres’ orbit.” The team’s infrared spectra support the conclusion that, like Ceres, the newly found asteroids have minerals on their surfaces that resulted from contact with liquid water. Furthermore, the circumstances in the solar nebula and the planetesimals in the early solar system are preserved by these dark asteroids.
“These are the remains of the building materials from which the planets of our solar system were created four and a half billion years ago,” said Dr. Mario Trieloff from the Institute of Earth Sciences in Heidelberg, Germany. He is part of the study team. “In these small bodies and their fragments, the meteorites, we find numerous relics that point directly to the process of planet formation.”
How Did Asteroid Water End Up on Earth?
Today’s planetary experts generally agree that many of Earth’s water sources were smaller bodies. They collided to form larger bodies, which collided with one another to form our globe. These “leftovers” from the solar system’s creation were dark, water-rich objects with water “inclusions”. Those might be minute fluid deposits or even icy strata within the rocks.
Or, they have “hydrated” minerals. Essentially, water exists inside them as part of the rock’s crystalline structure. Silicates (rocks that are mainly silicon and oxygen and make up much of Earth’s crust) are good examples of this. Some could have clay minerals (phyllosilicates). Certainly, many larger asteroids show evidence of these types of hydration. If you bring enough of them together, as happened with Earth’s formation, the water ends up at the growing body, along with the minerals.
These little worlds are also quite porous, which tells scientists they’re part of the original inventory of the solar system. “Shortly after the formation of the asteroids, temperatures were not high enough to convert them into a compact rock structure; they maintained the porous and primitive character typical of the outer ice planets located far from the sun,” explained Dr. Wladimir Neumann, a member of Prof. Trieloff’s team. That porosity also lends credence to their water-rich qualities.

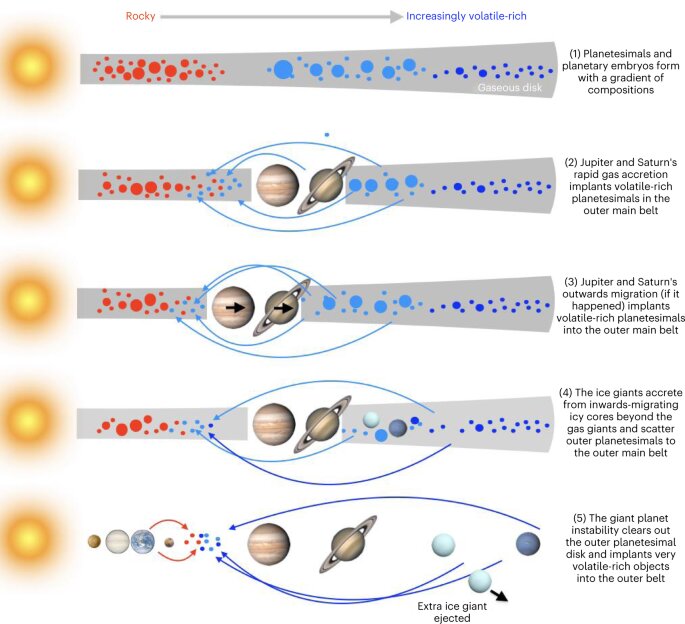
What Water-Rich Asteroids in the Belt Tell Us About Early Solar System History
The properties of the Ceres-like objects in the study and their presence in a relatively narrow zone of the outer Asteroid Belt have some interesting implications. They probably first formed in a cold region at the edge of our solar system, as Ceres likely did. Gravitational disruptions in the orbits of large planets like Jupiter and Saturn—or “giant planet instability”—changed the trajectory of these asteroids. Eventually, they ended up in today’s Asteroid Belt.

Like the smaller asteroids that resemble it by composition, Ceres has a water ice component. Some of that ice is in the surface layer and some is hidden inside. Deposits of ammonium salts near one of Ceres’s craters suggest it was born in the outer solar system. Perturbations caused by Jupiter’s migration to its present position also shifted Ceres to its present position. That sent this dwarf planet toward its current home in the Belt. Those same disturbances also moved other planetesimals and asteroids around. Eventually, they became part of other worlds closer to the Sun.
That ancient history is reflected today in Earth’s oceans and Mars’s current water-ice deposits. So, the next time you’re at the seashore, what you see was part of a bombardment of icy asteroids and comets. They delivered water from the outer regions of the solar system to the newly formed worlds of the inner solar system.
For More Information
Soucre: www.universetoday.com








