An international team of researchers has announced the discovery of two super-Earths orbiting the star LP 890-9. The find is interesting because the orbit of one of the planets passes in the so-called zone of life.
LP 890-9 is located at a distance of 100 light-years from Earth. It’s a cold red dwarf. Its radius is 6.5 times smaller than the radius of the Sun, and the surface temperature is only 2600 °C. During observations of the star, the TESS space telescope detected periodic decreases in its brightness corresponding to the transits of a body orbiting it with a period of 2.7 days.
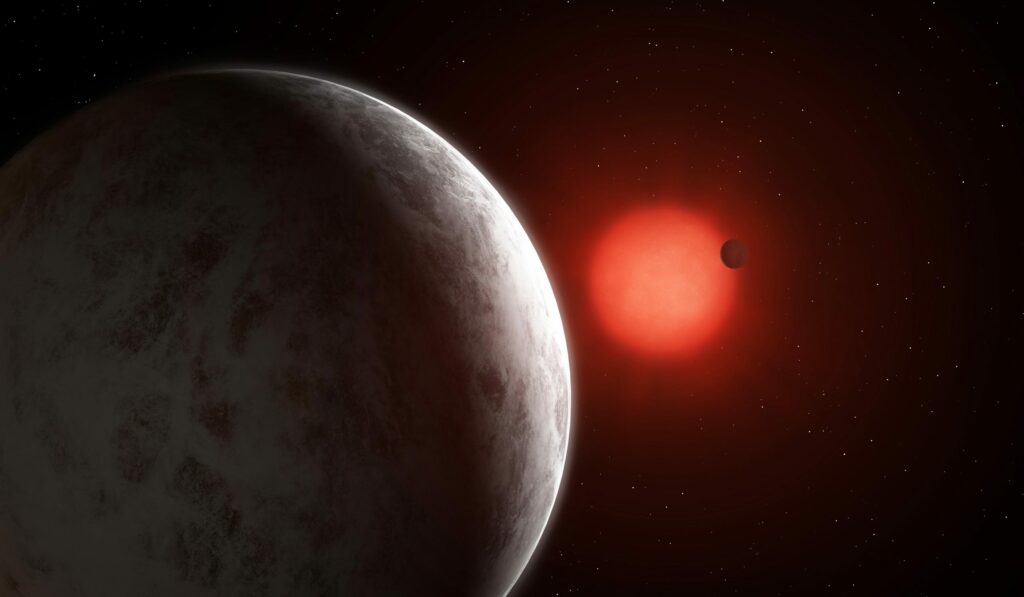

An exoplanet in the red dwarf system in the artist’s image. Source: Mark Garlick
In order to confirm the discovery, an international team of astronomers used the SPECULOOS complex. It consists of four automated telescopes located on top of the Chilean Cerro Paranal mountain. SPECULOOS managed not only to confirm the existence of the body found by TESS, but also to discover a second exoplanet.
Super-Earth in the zone of life
The first exoplanet, designated LP 890-9b, is a super-Earth. Its radius exceeds the radius of our planet by 30%, and its orbit passes at a distance of only 2.8 million km from the red dwarf. According to scientists, it receives 4.1 times more heat and light from its star than the Earth.
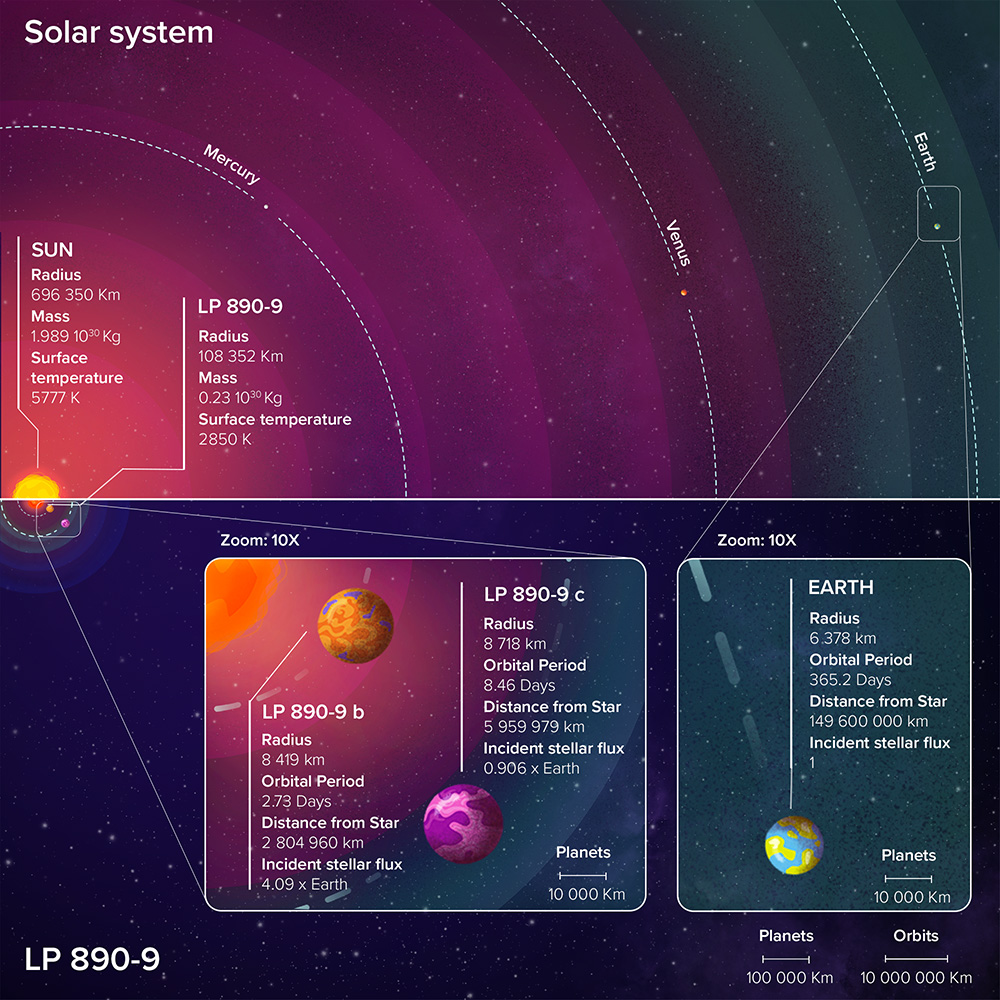
Characteristics of the stars and planets of the LP 890-9 system. Source: Adeline Deward (RISE-Illustration)
The second exoplanet (LP 890-9c) is also a super-Earth. Its radius is 40% larger than the radius of the Earth, and its orbit passes at a distance of 6 million km from the star. According to astronomers, its daytime hemisphere receives about 90% of the heat and light that our planet gets. This means that if there is a suitable atmosphere, liquid water can exist on the surface.
To test this assumption, in the future astronomers hope to use the James Webb Space Observatory to study this system. If LP 890-9c does have an atmosphere, the telescope will be able to find traces of it, and also try to determine its chemical composition.
Earlier we talked about how scientists created a three-dimensional portrait of a binary star system.
Theo https://www.news.uliege.be
Source: The Universe Space Tech








